# SQL Tables
# Tables
In relational databases, data is organized in tables. This example shows a table called “Customers”:
convention: table names sould be plural
In such a table, a column is an attribute, and a row is a dataentry.
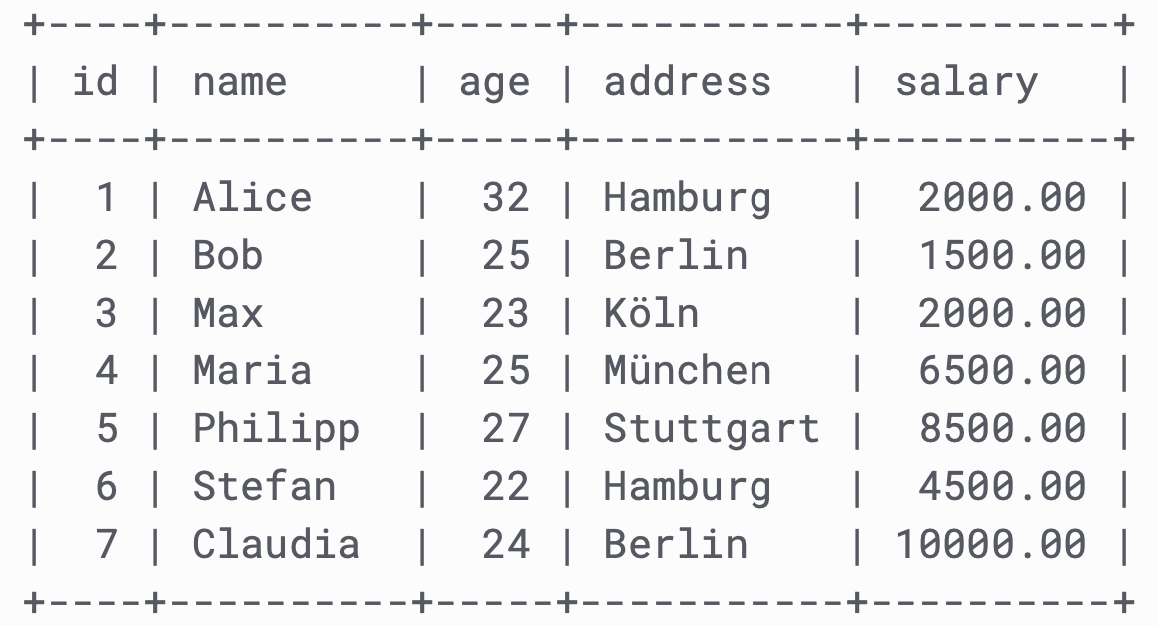
Look at a selection from the Northwind "Customers" table:
| CustomerID | CustomerName | ContactName | Address | City | PostalCode | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alfreds Futterkiste | Maria Anders | Obere Str. 57 | Berlin | 12209 | Germany |
| 2 | Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | Ana Trujillo | Avda. de la Constitución 2222 | México D.F. | 05021 | Mexico |
| 3 | Antonio Moreno Taquería | Antonio Moreno | Mataderos 2312 | México D.F. | 05023 | Mexico |
| 4 | Around the Horn | Thomas Hardy | 120 Hanover Sq. | London | WA1 1DP | UK |
| 5 | Berglunds snabbköp | Christina Berglund | Berguvsvägen 8 | Luleå | S-958 22 | Sweden |
The columns in the "Customers" table above are: CustomerID, CustomerName, ContactName, Address, City, PostalCode and Country. The table has 5 records (rows).
# Create a Table
convention: table-name is plural (lowercase, snake_case)
CREATE TABLE Customers(
id INT NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
age INT NOT NULL,
address TEXT,
salary DECIMAL (18, 2),
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
In general, the syntax is like this:
CREATE TABLE table_name(
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
.....
columnN datatype,
PRIMARY KEY( one or more columns )
);
# other example:
CREATE TABLE products (
id INT NOT NULL,
name STRING,
price MONEY,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
)
# Data Types
For each column, you need to define the data type. Common data types are:
INT - length 11 means 11 bytes
FLOAT
DECIMAL - DECIMAL(#digits, #digits after floating point)
BOOLEAN
VARCHAR - VARCHAR(length)
TEXT - any length
ENUM
DATE
BLOB - BINARY LARGE OBJECT. eg. (for images, but it's better to store a file-reference)
There is no boolean data type
https://www.w3schools.com/sql/sql_datatypes.asp (opens new window)
https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/data-types/ (opens new window)
# Data Type Specifications
Some data types you can specify even further:
| Specification | |
|---|---|
| UNSIGNED | only positive numbers |
| SIGNED | can have a sign (positive or negative) |
| NOT NULL | required - can not be null |
| AUTO_INCREMENT | if not set, increment automatically (used for IDs) |
# Primary Key
always needed - Primary keys must contain UNIQUE values, and cannot contain NULL values.
https://www.w3schools.com/sql/sql_primarykey.asp
-› assign a column
Every table needs one unique ID-field. This field (or column) is called the primary key.
You usually use integers for it. They need to be NOT NULL.
It is fine if IDs have "holes" - the just have to be unique
CREATE TABLE Customers(
id INT NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
age INT NOT NULL,
address TEXT,
salary DECIMAL (18, 2),
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
It is recommended to set this column to AUTO_INCREMENT. This means that if you don’t specify it for a new row, the database automatically sets it to a value that is the last value +1.
CREATE TABLE Customers(
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
...
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
# Show All Tables
Show all tables in a database:
SHOW TABLES;
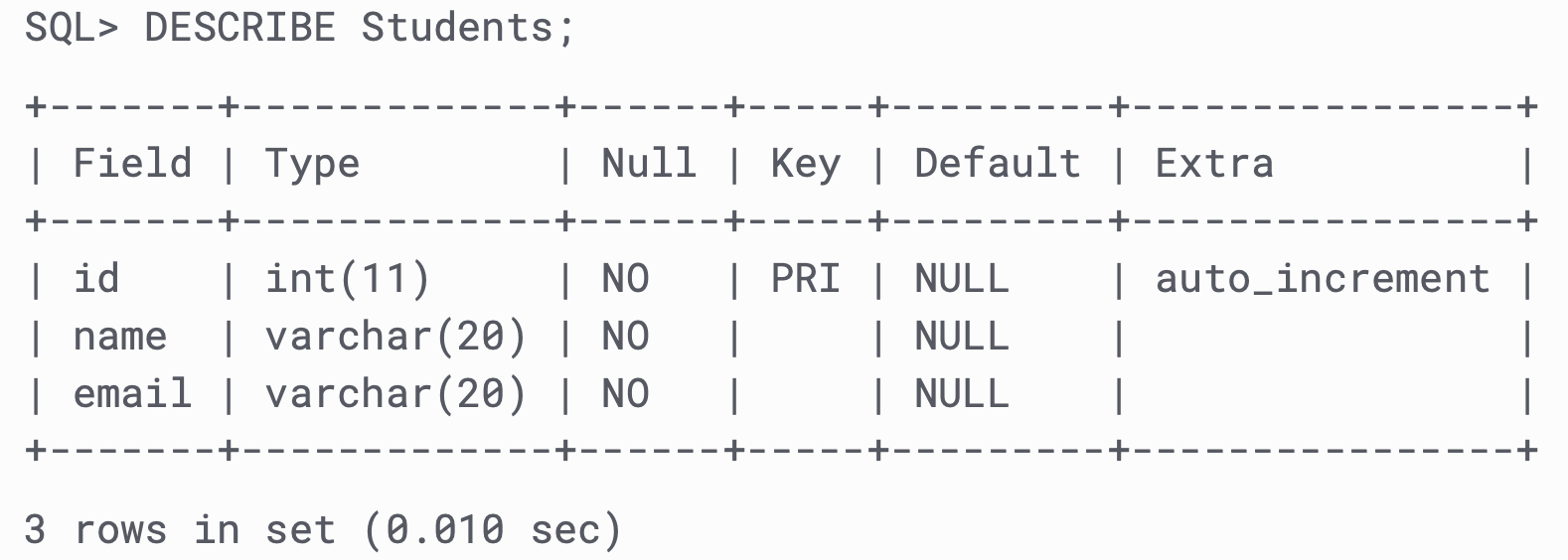
# Show Columns of a Table
DESCRIBE Students;